Hi! I'm a founding engineer at Compendium Labs. We're building interfaces for rapid and interactive generative AI. We also do contract work for folks looking to deploy (open or closed) LLMs at scale. I am an active contributor to open-source LLM projects such as llama.cpp.
I had a lengthy foray as an academic economist, and chances are I'll keep thinking and writing about such topics, though perhaps with more of a focus on the intersection of AI and economics. Check out my papers below!
First off, check out my GitHub page! There you can find code relating to the above papers, the below listed projects, and other side projects.
Stuck in LaTeX/PDF hell? There may be a way out. Nowadays, academics are relying less and less on the printed page. At the same time, there have been major advances in the speed and functionality of web technology, particularly in the mobile space. Check out the live demo above!
Elltwo is a browser based platform for decentralized and collaborative technical documents. It has a wiki like structure with an emphasis on typesetting and intelligent referencing. Articles are written in a simple markup language borrowing elements of Markdown and LaTeX.
Fastreg is a Python library for running high-dimensional regressions quickly using sparse matrix representations. It works quite well for regular old regressions too. Regression specifications can be described using a powerful new "Pythonic" syntax, in addition to the usual R-style syntax. Supported methods include OLS (with clustered standard errors), GLM, Poisson, maximum likelihood for arbitrary models, and more. See the GitHub link for examples and documentation.
This is a fully-featured USPTO patent data fetcher and parser written in Python. It can handle applications, grants, assignments, and maintenance events in all formats. Additionally, it can cluster firm names into groups that are suffiently similar. The clustering algorithm first filters potential matches using locality-sensitive hashing then generates clusters from the components of a graph induced by a given Levenshtein distance threshhold.
Cars can be pretty dangerous to bicyclists and pedestians! So I like to keep a close eye on them. With Speedcam, you can use a regular webcam as a speedometer. It will track cars in real time using YOLOv5 object detection combined with a Kalman filter and report their estimated speed. Check out the blog post above and go to the GitHub link to try it out on your own. Here's an example track:

This is a GNOME Shell plugin that provides a miniature preview of a chosen window, kind of like picture-in-picture on TVs. Great for watching movies while you're working, or at least pretending to.
Due to a preternaturally poor memory, I am an avid note taker. There are many, many note-taking apps out there, but not all focus on the other side of the equation: note-getting. Fuzzy is optimized for rapidly inputting and searching through notes, which comprise a title, a body of text, and a list of tags. The interface is web-based, but can be operated using only a keyboard.
Below is a service that allows you to look at the cumulative relative editing activity for a large number of tokens (about 1.1M) appearing in Wikipedia. You can type in your own (single) words into the box below, separated by commas, and see the results by pressing enter. You can also download the results in CSV form by clicking the button.
If you'd like to download the full dataset of tokens, just send me an email and I can arrange it. Even finer data is available at the article editing level.
This project is quite old. The goal was to investigate the evolution of cellular automata entities in a competitive setting. Below is the progress of a randomly generated trial run:
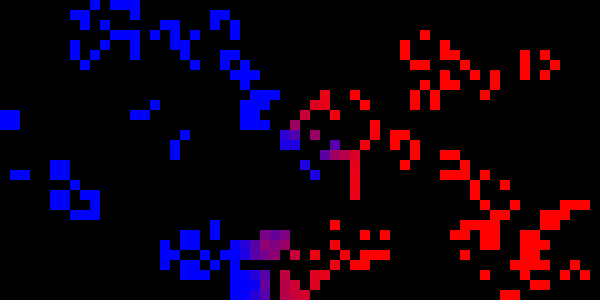
Below are lectures notes for some of the classes that I've taught over the years, both at the graduate and undergraduate level.
External website: doughanley.com/grad_macro
External website: doughanley.com/grad_comp
1 — Neoclassical Growth [HTML] [PDF]
2 — Endogenous Growth [HTML] [PDF]
3 — Schumpeterian Framework [HTML] [PDF]
1 — Preferences and Utility [PDF]
2 — The Walrasian Model and Consumer Choice [PDF]
3 — Consumer Demand [PDF]
4 — Equilibrium and Effiency [PDF]
5 — Equilibrium with Production [PDF]
6 — Firms and Production [PDF]
7 — Monopoly and Oligopoly [PDF]
8 — Intertemporal Choice and Uncertainty [PDF]
9 — Risk Sharing and Public Goods [PDF]
Advances in computing are critical for expanding the set of models that we can feasibly investigate quantitatively. GPU's are highly parallelized processing units, originally designed for use in video games, but increasingly finding their way into high performance computing. I gave a lecture in 2011 at Penn detailing how economists might use these in their research. The field is of course evolving rapidly on both the hardware and software fronts, so this may not incorporate all recent changes.

